
Next: Data
Up: Methods
Previous: Potential source contribution function
In this method, a mean or logarithmic mean concentration is calculated for
each grid cell 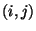 . The equation for the logarithmic mean is
. The equation for the logarithmic mean is
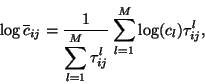 |
(2) |
where 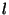 is the index of the trajectory,
is the index of the trajectory, 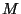 is the total number of
trajectories,
is the total number of
trajectories, 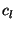 is the concentration observed on arrival of trajectory
is the concentration observed on arrival of trajectory
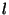 , and
, and 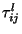 is the time spent in
is the time spent in 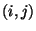 by trajectory
by trajectory 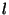 (Seibert et al., 1994; Stohl, 1998). A high value of
(Seibert et al., 1994; Stohl, 1998). A high value of
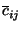 implies that air parcels travelling over
implies that air parcels travelling over 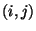 will have, on average,
high concentrations at the receptor.
will have, on average,
high concentrations at the receptor.
If the sampling time and/or the frequency of available trajectories are
not constant, we make, after reindexing, the following adjustment to the
weights in Eq. 2,
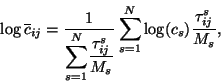 |
(3) |
where 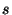 is the index of the sample,
is the index of the sample, 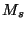 is the number of
trajectories arriving at the receptor site during the sampling time of
sample
is the number of
trajectories arriving at the receptor site during the sampling time of
sample 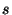 ,
, 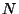 is the total number of samples, and
is the total number of samples, and 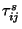 is the
total time spent in
is the
total time spent in 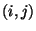 by the
by the 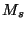 trajectories. If trajectory
data endpoints are given at equal time intervals,
trajectories. If trajectory
data endpoints are given at equal time intervals, 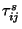 can be
replaced by the corresponding number of trajectory segment endpoints,
can be
replaced by the corresponding number of trajectory segment endpoints,
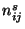 . When the sampling time is the same for all samples and the
frequency of trajectories is constant, Eq. 3 reduces to
Eq. 2.
. When the sampling time is the same for all samples and the
frequency of trajectories is constant, Eq. 3 reduces to
Eq. 2.


Next: Data
Up: Methods
Previous: Potential source contribution function
Alexandru Lupu
2002-08-20