The
Migration Policy Index
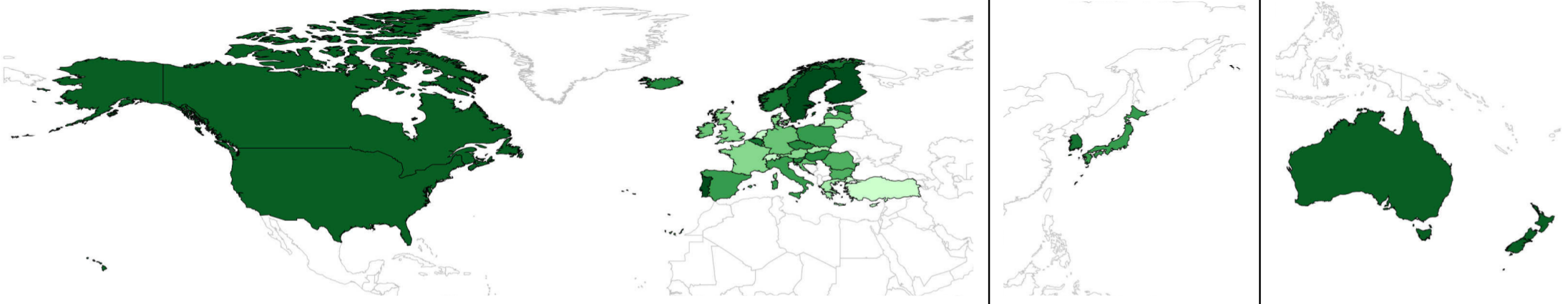
Plot of the (overall) MPI values in
2014, with darker colors indicating a less restrictive policy
Source: Rayp, Ruyssen and Standaert, 2017
Source: Rayp, Ruyssen and Standaert, 2017
About
The Migration Policy Index is a
composite index reflecting the de jure openness of migration
policy. It summarizes all available indicators informative of economic
migration, excluding those that apply strictly to asylum policy.
Importantly, this index does not contain any de facto
information, like the number of migrants received, as this would
confuse the outcome of a country’s immigration laws rather than
their intended objectives. In addition to an overall index, we also
composed three sub-indexes that track entry policies (including family
reunification), stay policies (permanent as opposed to temporary
migration); and integration policies (including migrant rights). For
more information on the construction of the MPI, we refer to the paper
listed below.
Cite
Please cite as: Glenn Rayp, Ilse
Ruyssen and Samuel Standaert (2017), "Measuring and Explaining
Cross-Country Immigration Policies", World Development, Vol.
95, pp. 141--163.
Download
Click
here to download the worldwide MPI indexes in csv format. This
file contains the following variables:
- id: a numerical country id
- iso: the 3 digit ISO codes
- name: the country names
- year
The file also contains the following information for the overall index (MPI) and each of the sub-indexes: Entry (MPI_E), Stay (MPI_S) and Integration legislation (MPI_I).
- MPI: the index values
- stdDev: the standard deviation of each estimate
- rank: ranking of countries per year, based on significant differences
- nrVars: number of individual indicators available in that year used to compute the index
 |

|